Countering Counterfeit Currency: Safeguarding Peshawar’s Financial Integrity
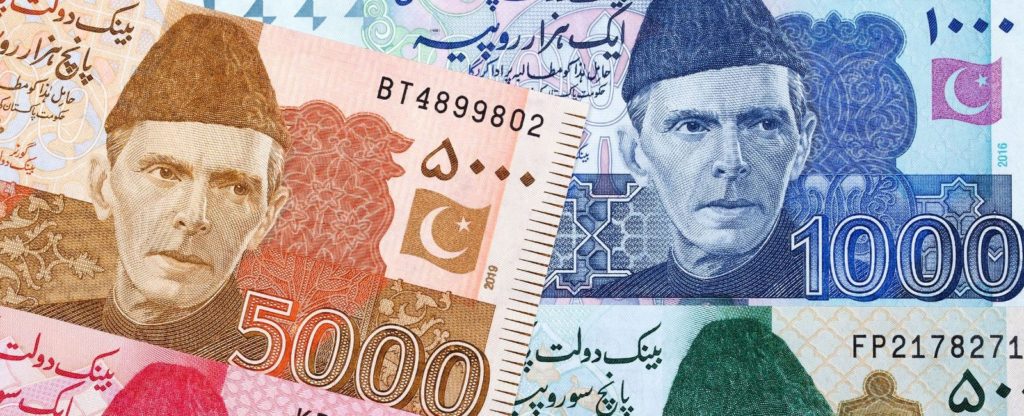
counterfeit currency in peshawar , the historic capital of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, stands as a vibrant hub of commerce and culture. Yet, amidst its bustling markets and bustling streets, lurks a shadowy threat – counterfeit currency. The proliferation of fake banknotes not only undermines the city’s economic stability but also erodes trust in its financial institutions. This article delves into the clandestine world of counterfeit currency in Peshawar, exploring its origins, impacts, and the strategies employed to combat this pervasive menace.
The Genesis of Counterfeit Currency:
Counterfeit currency, a perennial challenge faced by economies worldwide, has found a foothold in Peshawar’s markets. Advances in printing technology and the widespread availability of instructional materials online have emboldened counterfeiters to produce fake banknotes with alarming precision. Additionally, porous borders and weak enforcement mechanisms create fertile ground for the circulation of counterfeit currency within Peshawar’s economy.
Impacts on Economy and Society:
The consequences of counterfeit currency extend beyond monetary losses, casting a shadow over Peshawar’s economic landscape. Small businesses, vital to the city’s economy, often bear the brunt of this illicit trade, facing financial hardships and diminished consumer trust. For ordinary citizens, receiving counterfeit money not only diminishes purchasing power but also fosters mistrust in the banking system. Furthermore, the circulation of fake currency poses a systemic risk, potentially destabilizing Peshawar’s economy and deterring foreign investment.
Law Enforcement Efforts:
Countering counterfeit currency demands a concerted effort from law enforcement agencies. In Peshawar, authorities such as the Federal Investigation Agency (FIA) and the State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) have intensified their efforts to combat counterfeiters, conducting raids and implementing stringent anti-counterfeiting measures. However, the clandestine nature of this illicit trade presents significant challenges, necessitating innovative strategies and collaboration with the public.
Public Awareness and Vigilance:
Empowering citizens with knowledge about the security features of genuine banknotes is crucial in the fight against counterfeit currency. Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives can equip individuals with the skills to detect and report counterfeit money effectively. Additionally, promoting the use of counterfeit detection devices and encouraging digital payment methods can mitigate the risk of falling victim to counterfeiters.
Collaborative Solutions:
Safeguarding Peshawar’s economy against counterfeit currency requires a collaborative approach involving government agencies, businesses, and the community at large. Strengthening cooperation between law enforcement agencies and financial institutions can enhance the detection and apprehension of counterfeiters. Furthermore, fostering transparency and accountability within the banking sector can serve as a deterrent against illicit activities.
Conclusion: Counterfeit currency poses a significant threat to Peshawar’s economic prosperity and social fabric. Addressing this pervasive issue demands a comprehensive strategy, encompassing robust law enforcement measures, public awareness campaigns, and collaborative initiatives. By uniting against the scourge of counterfeit currency, Peshawar can preserve its economic integrity and uphold the trust and confidence of its citizens and investors alike.